Chronic social defeat stress impairs goal-directed behavior through dysregulation of ventral hippocampal activity in male mice
Title: Chronic social defeat stress impairs goal-directed behavior through dysregulation of ventral hippocampal activity in male mice
Authors: Keitaro Yoshida, Michael R. Drew, Anna Kono, Masaru Mimura, Norio Takata & Kenji F. Tanaka
Journal: Neuropsychopharmacology, Vol 46, Issue 9, Page 1606-1616 (2021)
DOI: 10.1038/s41386-021-00990-y
Abstract:
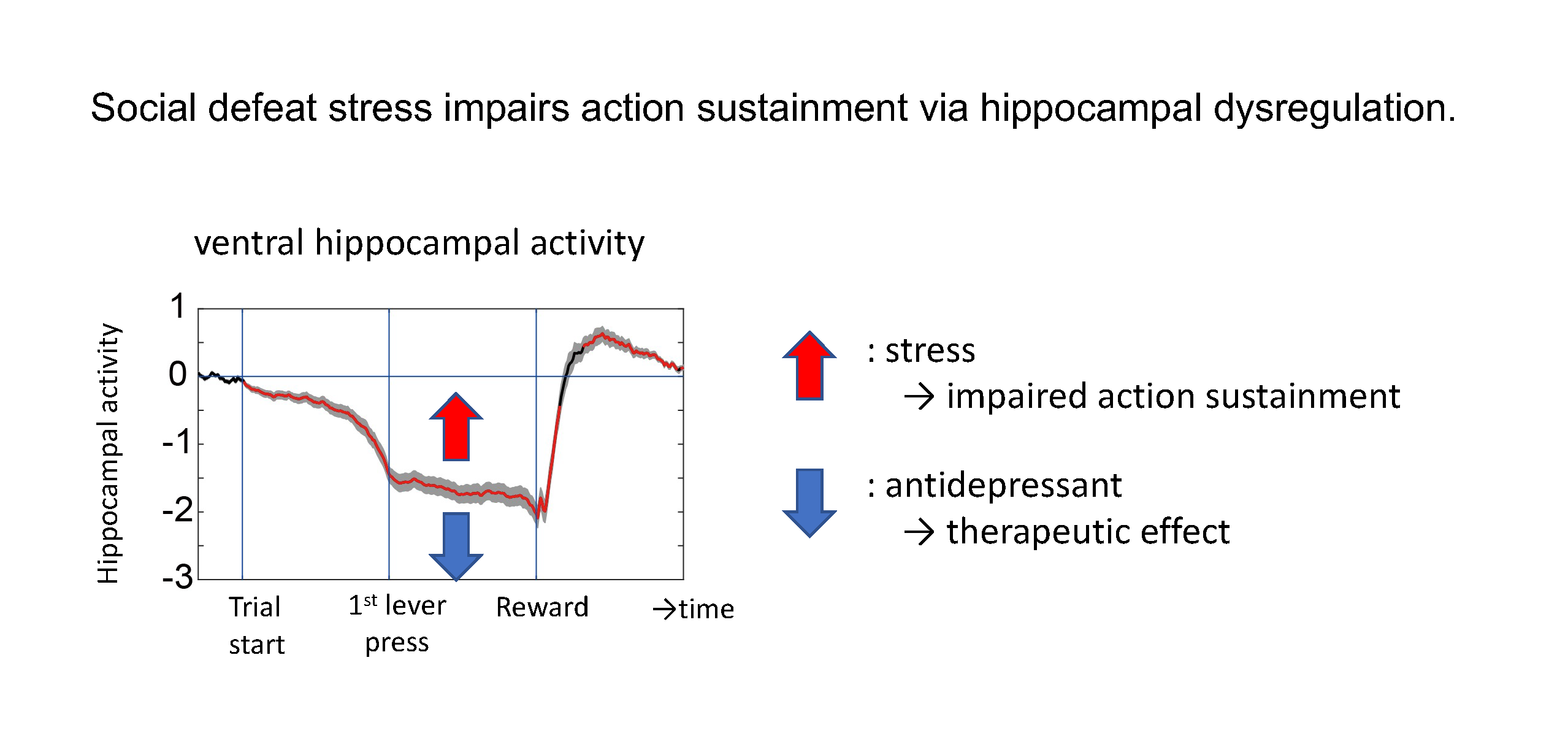
Chronic stress is a risk factor for a variety of psychiatric disorders, including depression. Although impairments to motivated behavior are a major symptom of clinical depression, little is known about the circuit mechanisms through which stress impairs motivation. Furthermore, research in animal models for depression has focused on impairments to hedonic aspects of motivation, whereas patient studies suggest that impairments to appetitive, goal-directed motivation contribute significantly to motivational impairments in depression. Here, we characterized goal-directed motivation in repeated social defeat stress (R-SDS), a well-established mouse model for depression in male mice. R-SDS impaired the ability to sustain and complete goal-directed behavior in a food-seeking operant lever-press task. Furthermore, stress-exposed mice segregated into susceptible and resilient subpopulations. Interestingly, susceptibility to stress-induced motivational impairments was unrelated to stress-induced social withdrawal, another prominent effect of R-SDS in mouse models. Based on evidence that ventral hippocampus (vHP) modulates sustainment of goal-directed behavior, we monitored vHP activity during the task using fiber photometry. Successful task completion was associated with suppression of ventral hippocampal neural activity. This suppression was diminished after R-SDS in stress-susceptible but not stress-resilient mice. The serotonin selective reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) escitalopram and ketamine both normalized vHP activity during the task and restored motivated behavior. Furthermore, optogenetic vHP inhibition was sufficient to restore motivated behavior after stress. These results identify vHP hyperactivity as a circuit mechanism of stress-induced impairments to goal-directed behavior and a putative biomarker that is sensitive to antidepressant treatments and that differentiates susceptible and resilient individuals.
Related Articles:
- Opposing Ventral Striatal Medium Spiny Neuron Activities Shaped by Striatal Parvalbumin-Expressing Interneurons during Goal-Directed Behaviors. Cell Reports, Vol. 31, Issue. 13, 107829 (2020). DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107829
- Serotonin-mediated inhibition of ventral hippocampus is required for sustained goal-directed behavior. Nature Neuroscience, Vol. 22, Issue. 5, pp. 770-777 (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41593-019-0376-5
- Dysfunction of ventrolateral striatal dopamine receptor type 2-expressing medium spiny neurons impairs instrumental motivation. Nature Communications, Vol. 8, 14304 (2017). DOI: 10.1038/ncomms14304





