Simultaneous crosslinking induces macroscopically phase-separated microgel from a homogeneous mixture of multiple polymers
Title: Simultaneous crosslinking induces macroscopically phase-separated microgel from a homogeneous mixture of multiple polymers
Authors: Yuta Kurashina, Mio Tsuchiya, Atsushi Sakai, Tomoki Maeda, Yun Jung J. Heo, Filippo Rossi, Nakwon Choi, Miho Yanagisawa, Hiroaki Onoe
Journal: Applied Materials Today, Vol 22, Number 100937 (2021)
DOI: 10.1016/j.apmt.2021.100937
Abstract:
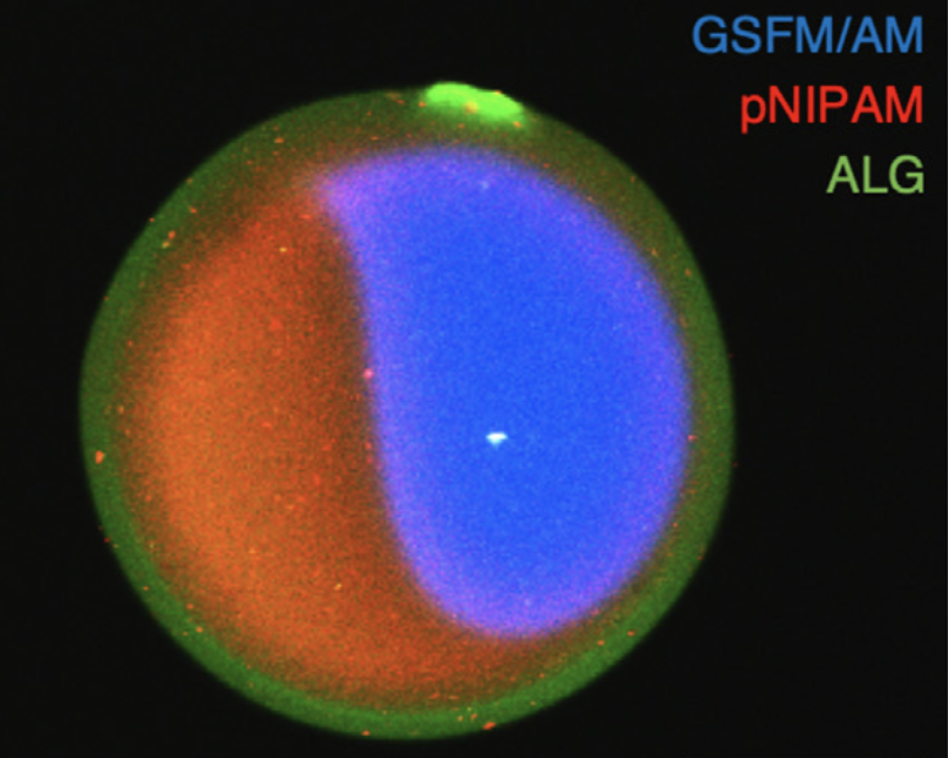
This paper reports a unique phase separation behavior, a simultaneous-crosslinking-driven phase separation in co-gelation (SPSiC) core-shell microgel that spontaneously forms from a homogeneous pre-gel solution of multiple polymers. The SPSiC microgel, composed of an alginate shell and an N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAM) core, were synthesized by a single fabrication step wherein a mixed pre-gel solution of sodium alginate and NIPAM monomer was ejected by centrifugation with photo-polymerization and ion crosslinking instantaneously. Phase separation was modeled by varying the degree of polymerization and the size of the polymer chain. Moreover, an implantable, multi-functional drug delivery system combined with a transdermal glucose sensor was demonstrated with core-shell Janus SPSiC microgels. This work shows a macroscopic phase separation behavior, which occurs during the gelation process, and also provides a simple and unique methodology to create multifunctional bio-microprobes.
Related Articles:
- Eye-recognizable and repeatable biochemical flexible sensors using low angle-dependent photonic colloidal crystal hydrogel microbeads. Scientific Reports, Vol. 9, 17059 (2019). DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-53499-2
- Ultrasound-triggered on-demand drug delivery using hydrogel microbeads with release enhancer. Materials & Design, Vol. 203, 109580 (2021). DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2021.109580
- Janus hydrogel microbeads for glucose sensing with pH calibration. Sensors, Vol. 21, Issue. 14, 4829 (2021). DOI: 10.3390/s21144829





