Role of Nampt-Sirt6 Axis in Renal Proximal Tubules in Extracellular Matrix Deposition in Diabetic Nephropathy
Title: Role of Nampt-Sirt6 Axis in Renal Proximal Tubules in Extracellular Matrix Deposition in Diabetic Nephropathy
Authors: Hirokazu Muraoka, Kazuhiro Hasegawa, Yusuke Sakamaki, Hitoshi Minakuchi, Takahisa Kawaguchi, Itaru Yasuda, Takeshi Kanda, Hirobumi Tokuyama, Shu Wakino and Hiroshi Itoh
Journal: Cell Reports, Volume 27, Issue 1, P199-212.E5 (2019)
DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.03.024
Abstract:
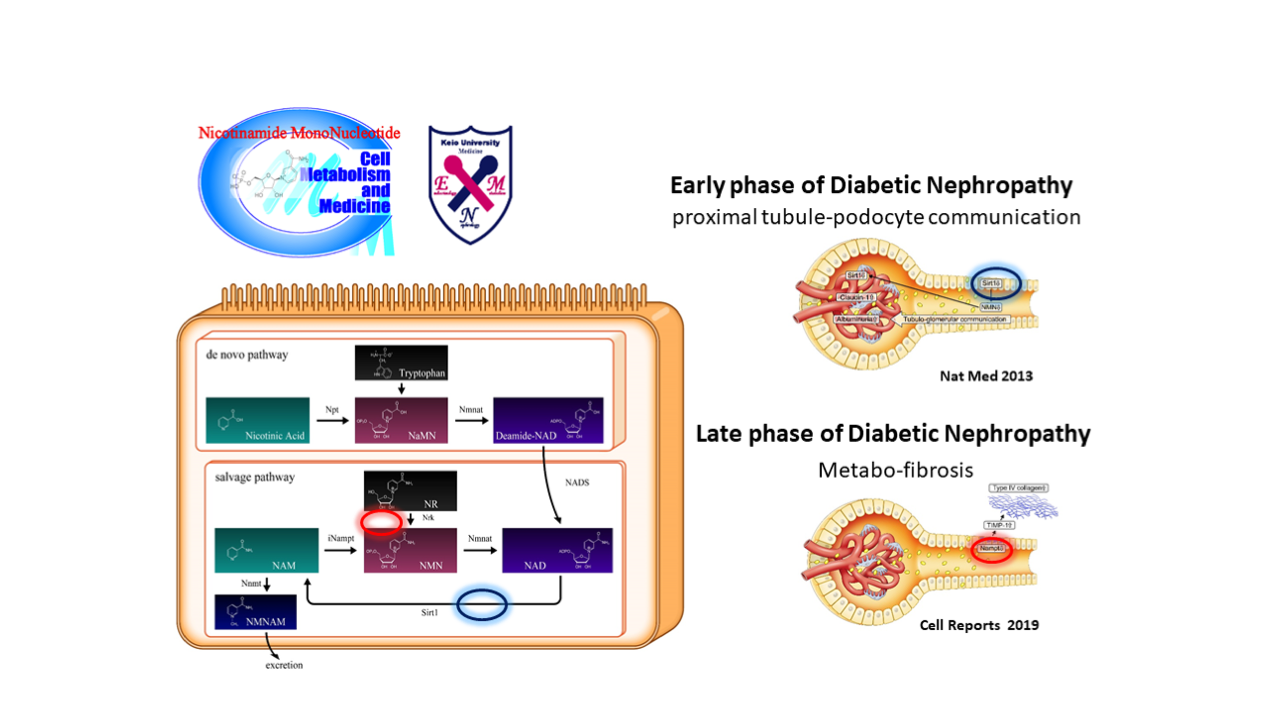
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) metabolism plays a critical role in kidneys. We previously reported that decreased secretion of a NAD+ precursor, nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), from proximal tubules (PTs) can trigger diabetic albuminuria. In the present study, we investigated the role of NMN-producing enzyme nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (Nampt) in diabetic nephropathy. The expression of Nampt in PTs was downregulated in streptozotocin (STZ)-treated diabetic mice when they exhibited albuminuria. This albuminuria was ameliorated in PT-specific Nampt-overexpressing transgenic (TG) mice. PT-specific Nampt-conditional knockout (Nampt CKO) mice exhibited TBM thickening and collagen deposition, which were associated with the upregulation of the profibrogenic gene TIMP-1. Nampt CKO mice also exhibited the downregulation of sirtuins, particularly in Sirt6. PT-specific Sirt6-knockout mice exhibited enhanced fibrotic phenotype resembling that of Nampt CKO mice with increased Timp1 expression. In conclusion, the Nampt-Sirt6 axis in PTs serves as a key player in fibrogenic extracellular matrix remodeling in diabetic nephropathy.





