Human-specific ARHGAP11B increases size and folding of primate neocortex in the fetal marmoset
Title: Human-specific ARHGAP11B increases size and folding of primate neocortex in the fetal marmoset
Authors: Michael Heide, Christiane Haffner, Ayako Murayama, Yoko Kurotaki, Haruka Shinohara, Hideyuki Okano, Erika Sasaki, Wieland B. Huttner
Journal: Science, 369(6503):546-550 (2020)
DOI: 10.1126/science.abb2401
Abstract:
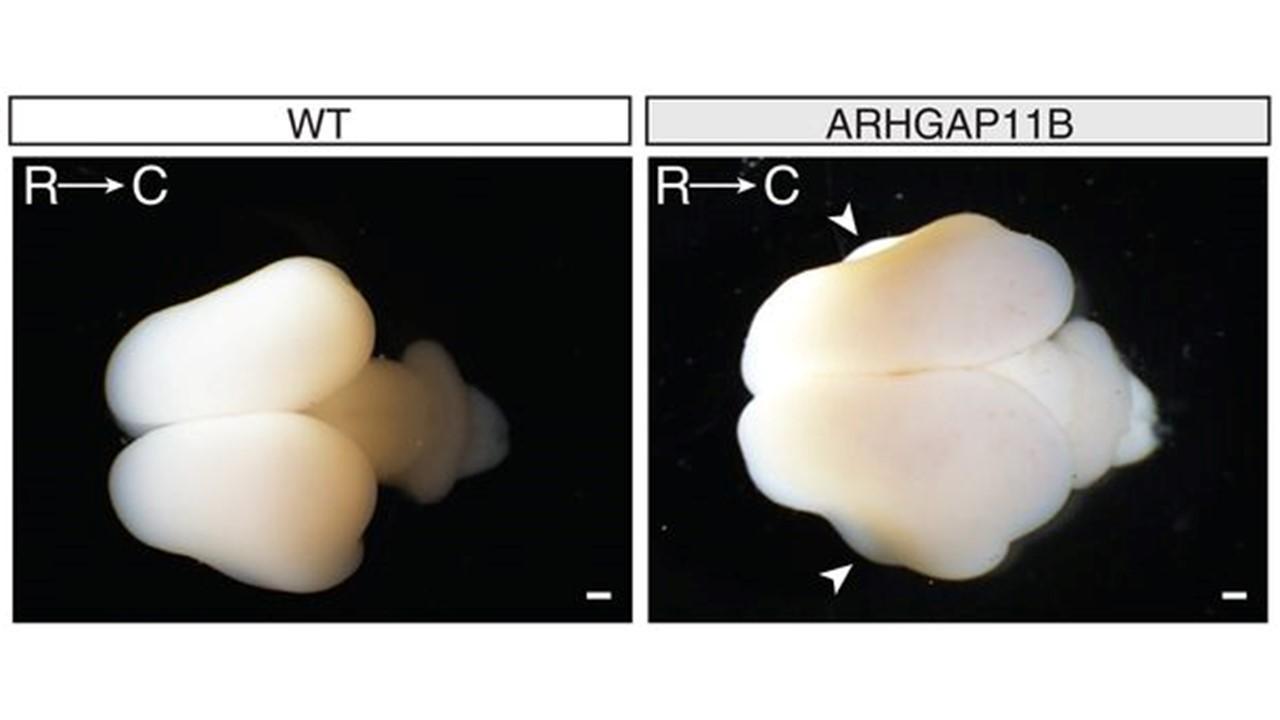
The neocortex has expanded during mammalian evolution. Overexpression studies in developing mouse and ferret neocortex have implicated the human-specific gene ARHGAP11B in neocortical expansion, but the relevance for primate evolution has been unclear. Here, we provide functional evidence that ARHGAP11B causes expansion of the primate neocortex. ARHGAP11B expressed in fetal neocortex of the common marmoset under control of the gene's own (human) promoter increased the numbers of basal radial glia progenitors in the marmoset outer subventricular zone, increased the numbers of upper-layer neurons, enlarged the neocortex, and induced its folding. Thus, the human-specific ARHGAP11B drives changes in development in the nonhuman primate marmoset that reflect the changes in evolution that characterize human neocortical development.
関連論文:





